Private Non-Renewable Resource Model
Contents
Private Non-Renewable Resource Model¶
Randall Romero Aguilar, PhD
This demo is based on the original Matlab demo accompanying the Computational Economics and Finance 2001 textbook by Mario Miranda and Paul Fackler.
Original (Matlab) CompEcon file: demdp09.m
Running this file requires the Python version of CompEcon. This can be installed with pip by running
!pip install compecon --upgrade
Last updated: 2022-Oct-23
About¶
Profit maximizing mine owner must decide how much ore to extract
States
s: ore stock
Actions
q: ore extracted and sold
Parameters
a0,a1: demand function parameters
b0,b1: supply function parameters
\(\delta\): discount factor
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from compecon import BasisSpline, DPmodel, DPoptions, qnwnorm
Model parameters¶
a0, a1, b0, b1, δ = 5, 0.8, 7, 1.0, 0.9
State space¶
The state variable is s=”Stock”, which is restricted to \(s\in[0, 10]\).
Here, we represent it with a cubic spline basis, with \(n=101\) nodes.
n, smin, smax = 101, 0, 10
basis = BasisSpline(n, smin, smax, labels=['Ore Stock'])
Action space¶
The choice variable q=”Ore extracted” must be nonnegative.
def bounds(s, i=None, j=None):
return np.zeros_like(s), s[:]
Reward function¶
The reward function is the utility of harvesting \(q\) units.
def reward(s, q, i=None, j=None):
u = (a0-b0+b1*s)*q - (a1+b1/2)*q**2
ux = (a0-b0+b1*s) - (2*a1+b1)*q
uxx = -2*(a1+b1/2)*np.ones_like(s)
return u, ux, uxx
State transition function¶
Next period, the stock will be equal that is \(s' = \alpha (s-q) - 0.5\beta(s-q)^2\)
def transition(s, q, i=None, j=None, in_=None, e=None):
g = s-q
gx = -np.ones_like(s)
gxx = np.zeros_like(s)
return g, gx, gxx
Model structure¶
The value of wealth \(s\) satisfies the Bellman equation
To solve and simulate this model,use the CompEcon class DPmodel
model = DPmodel(basis, reward, transition, bounds,
x=['Ore Extracted'],
discount=δ)
Solving the model¶
Solving the growth model by collocation
S = model.solve()
S.head()
Solving infinite-horizon model collocation equation by Newton's method
iter change time
------------------------------
0 1.9e+01 0.0156
1 3.5e+00 0.0334
2 2.2e-01 0.0516
3 1.0e-03 0.0673
4 2.2e-08 0.0673
5 1.9e-14 0.0829
Elapsed Time = 0.08 Seconds
| Ore Stock | value | resid | Ore Extracted | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ore Stock | ||||
| 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000e+00 | 0.000000e+00 | 0.000000e+00 |
| 0.009911 | 0.009911 | -3.725252e-16 | -3.725252e-17 | 3.016346e-15 |
| 0.019822 | 0.019822 | -3.915019e-16 | -3.915019e-17 | 3.170001e-15 |
| 0.029732 | 0.029732 | -1.557981e-16 | -1.557981e-17 | 1.261501e-15 |
| 0.039643 | 0.039643 | 2.357181e-16 | 2.357181e-17 | -1.908615e-15 |
DPmodel.solve returns a pandas DataFrame with the following data:
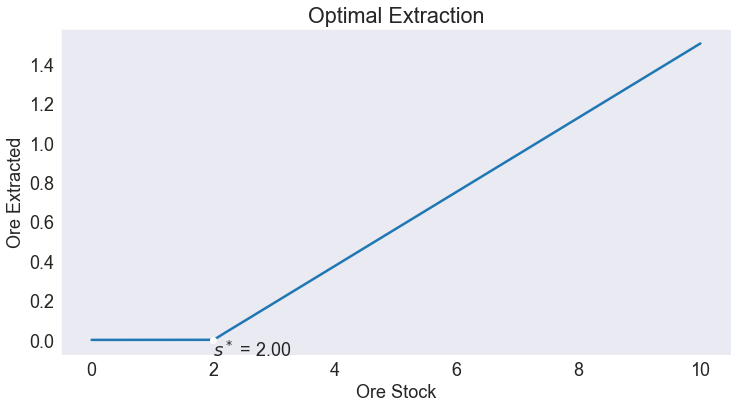
Compute and print abandonment point
sstar = (b0-a0)/b1
print(f'Abandonment Point = {sstar:5.2f}')
Abandonment Point = 2.00
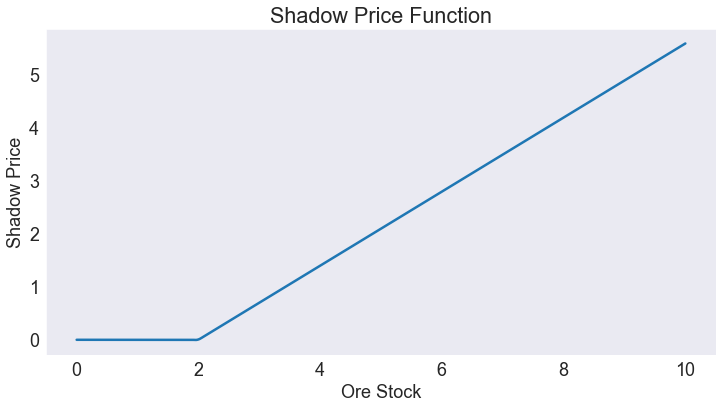
We are also interested in the shadow price of ore (the first derivative of the value function).
S['shadow price'] = model.Value(S['Ore Stock'],1)
Plotting the results¶
Optimal Policy¶
fig1, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.set(title='Optimal Extraction', xlabel='Ore Stock', ylabel='Ore Extracted')
ax.plot(S['Ore Extracted'])
ax.plot(sstar, 0, 'wo')
ax.annotate(f"$s^*$ = {sstar:.2f}",[sstar, 0], va='top');
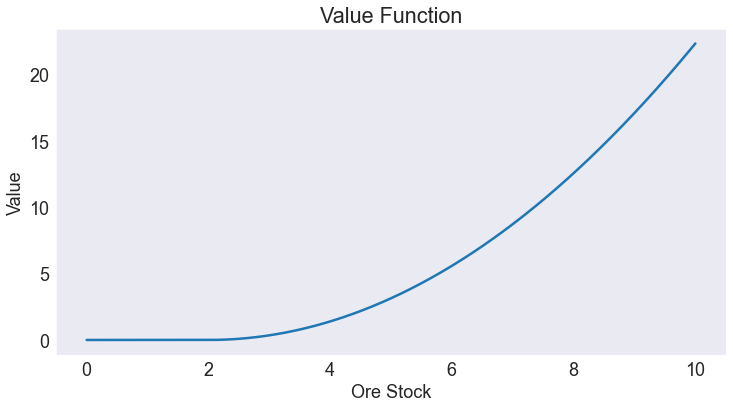
Value Function¶
fig2, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.set(title='Value Function', xlabel='Ore Stock', ylabel='Value')
ax.plot(S.value);
Shadow Price Function¶
fig3,ax = plt.subplots()
ax.set(title='Shadow Price Function', xlabel='Ore Stock', ylabel='Shadow Price')
ax.plot(S['shadow price']);
Residual¶
fig4, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.set(title='Bellman Equation Residual', xlabel='Ore Stock', ylabel='Residual')
ax.axhline(0, color='white')
ax.plot(S['resid'])
ax.ticklabel_format(style='sci', axis='y', scilimits=(-1,1))
Simulating the model¶
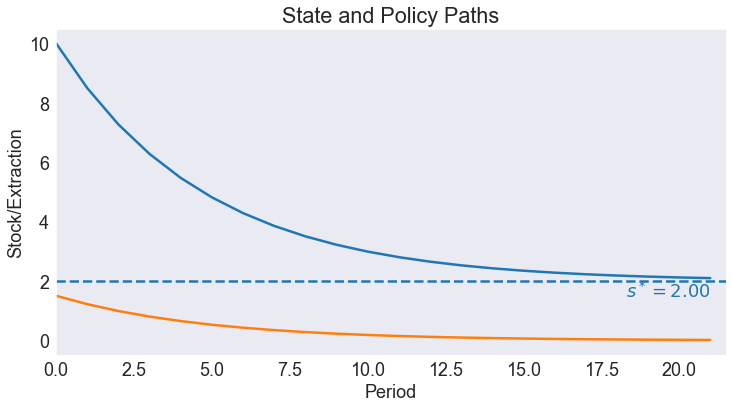
We simulate 21 periods of the model starting from \(s=s_{\max}\)
T = 21
data = model.simulate(T, smax)
data.head()
| time | Ore Stock | Ore Extracted | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 10.000000 | 1.506241 |
| 1 | 1 | 8.493759 | 1.222646 |
| 2 | 2 | 7.271113 | 0.992446 |
| 3 | 3 | 6.278667 | 0.805588 |
| 4 | 4 | 5.473079 | 0.653912 |
Simulated State and Policy Paths¶
fig5, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.set(title='State and Policy Paths',
xlabel='Period',
ylabel='Stock/Extraction',
xlim=[0, T + 0.5])
ax.plot(data[['Ore Stock', 'Ore Extracted']])
ax.axhline(sstar, linestyle='--')
ax.annotate(f'$s^* = {sstar:.2f}$', [T, sstar], ha='right', va='top', color='C0');